Overview
Trima Accel
Automated Blood Collection System
Reveos
Automated Blood Processing System
Welders & Sealers
Reliable, sterile connections using cost-effective tubing welders and sealers
Whole Blood Bag Systems
Whole blood collection, component processing and storage
Mirasol
Pathogen Reduction Technology (PRT) System
See all
Overview
Spectra Optia
Apheresis System
Therapeutic Plasma Exchange (TPE)
Exchange protocols available on the Spectra Optia Apheresis System
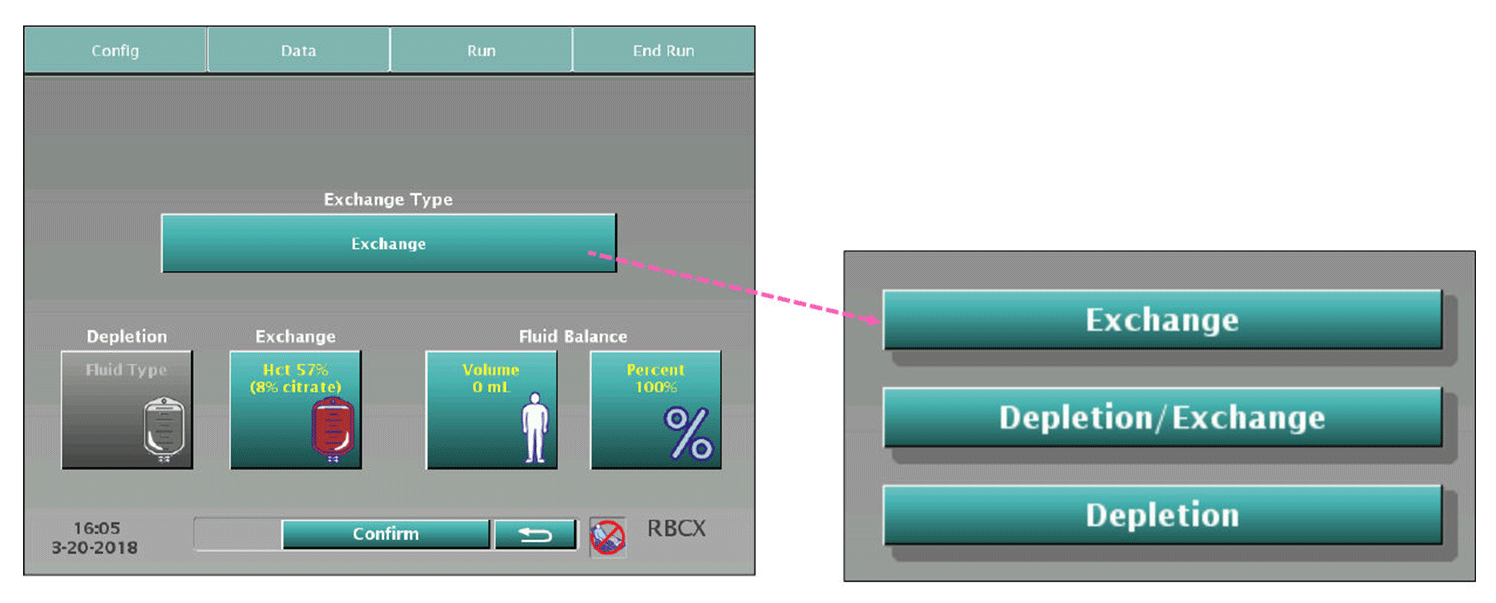
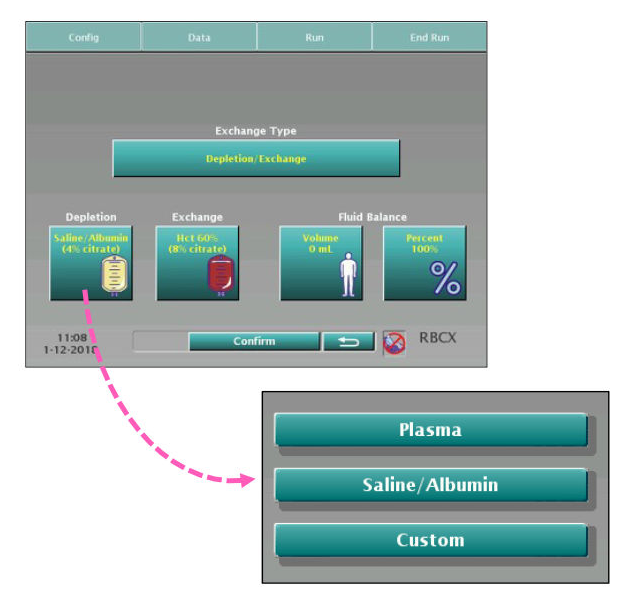
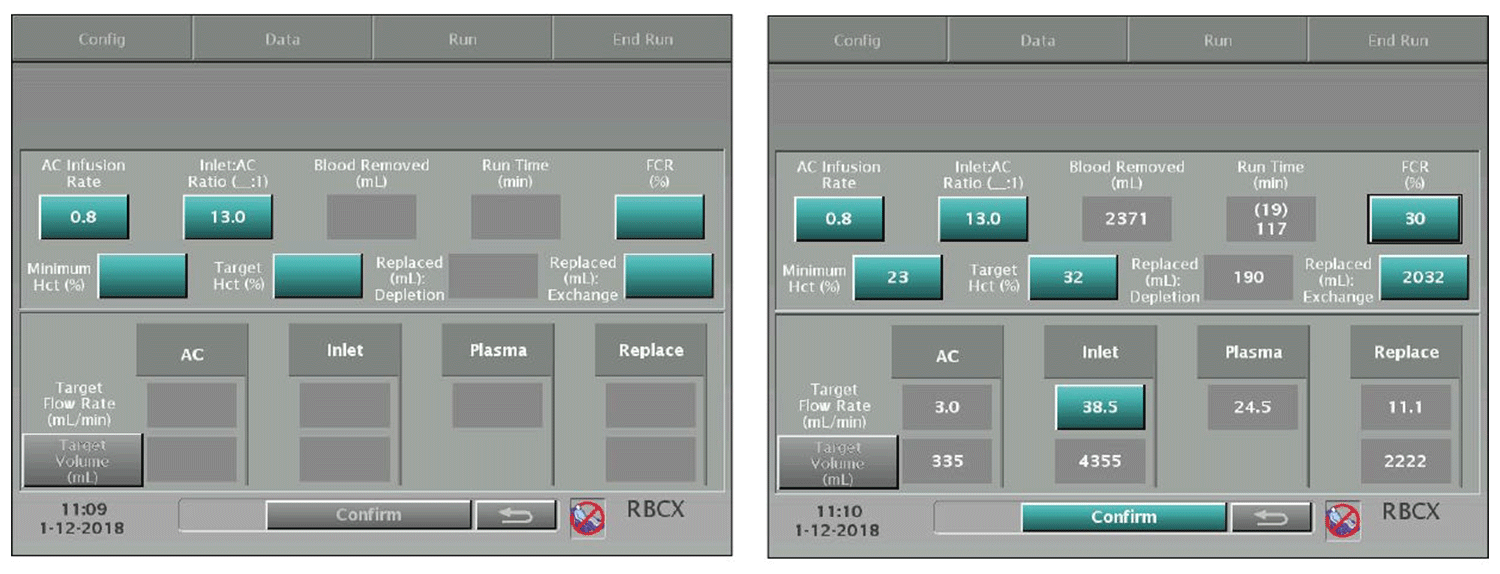
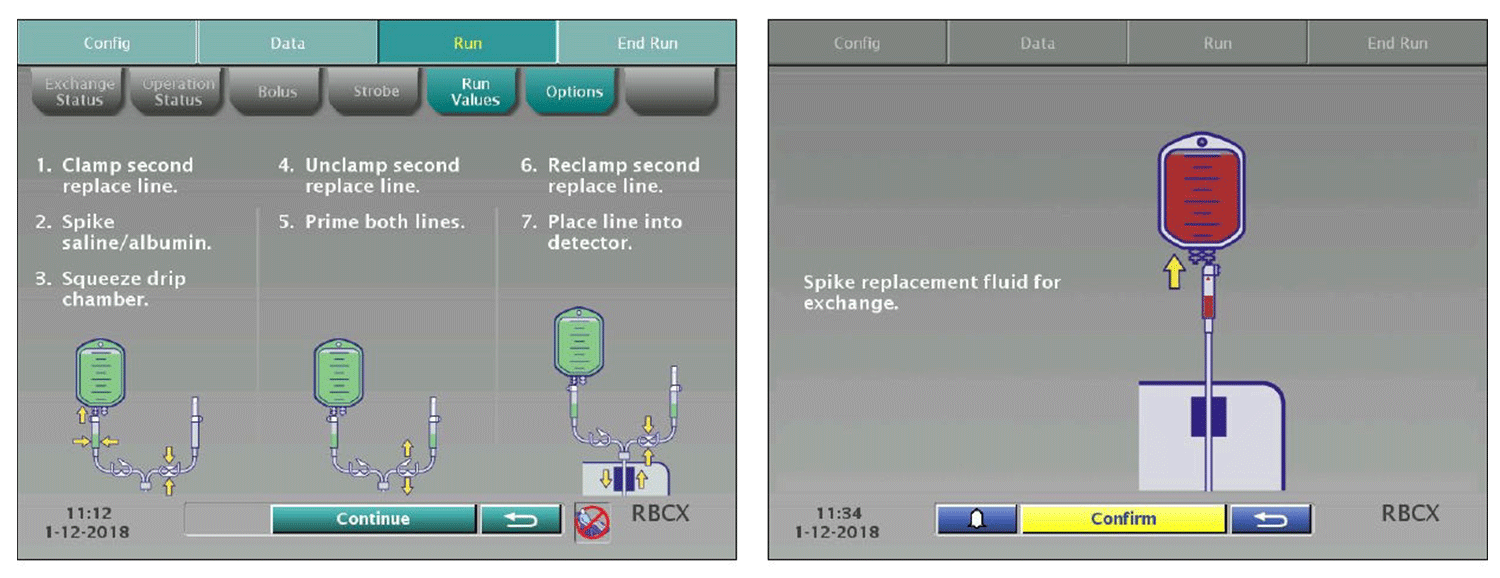
Red Blood Cell Exchange
Therapeutic Apheresis Red Blood Cell Exchange
Cell Collections
Comprehensive cell collection solutions
Vascular Access
Your resource for optimizing vascular access for each and every patient
Sickle Cell Disease
Transfusion Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
See all

/dog-with-no-spectra-optia.jpg)
/dog3.jpg)
/spectraoptia.jpg)